Emergency Contraception Methods can be used to prevent pregnancy if one had sex without using birth control or if the birth control method did not work correctly.
They must be used immediately after the unprotected sex. They are not the same as abortion pills and will not work in case you are already pregnant.
Types of Emergency Contraception Methods
- Levonorgestrel containing pills have to be taken within 72 hours (3 days) of sex to prevent pregnancy.
- Ulipristal acetate containing pills have to be taken within 120 hours (5 days) of sex to prevent pregnancy.
- IUD can be fitted up to 5 days after unprotected sex, or up to 5 days after the earliest time you could have ovulated, for it to be effective.
Mechanism Of Action
- They prevent or delay ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovary).
- They prevent fertilization of the egg by the sperm if ovulation has already happened
Who should consider Emergency Contraception?
- If you had unprotected sex.
- Or you used a method, but it failed, for e.g. the condom tore or slipped off.
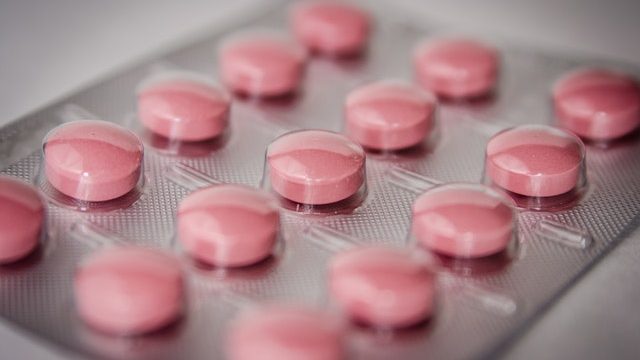
Emergency Contraceptive Pills
Effect of the pills on the periods
The next period may come early or late, and one may have spotting or flow may be heavier or lighter than normal.
If the period does not come for a week from the expected date, then it is advisable to check for pregnancy.
It is prudent to check for pregnancy even if the period is lighter and or shorter than the regular period, or one has severe abdominal pain and an abnormal flow.
Important Facts about Emergency Contraceptive Pills
- To be effective they need to be taken as soon as possible after the unprotected sex.
- They may not be as effective for women with a BMI of more than 30 as for women with less BMI.
- They do not protect against sexually transmitted infections.
- If one vomits within two hours of taking the pill then one may need to take an additional dose.
- They should not be used as a regular form of contraception, But one can use emergency contraception more than once in a menstrual cycle if required.
- These tablets may interact with certain antibiotics, TB medicines, HIV medicines, and anti-epileptic drugs.
- Levonorgestrel containing tablets are safe while breastfeeding but it is advisable to avoid breastfeeding if one takes ulipristal acetate tablets.
- Side effects may include headache abdominal pain tiredness (fatigue) dizziness nausea and breast pain.
- The side effects are usually mild and do not last long.
Important Facts About IUD As Emergency Contraceptive
- The IUD can be left in and continued as your regular contraceptive method.
- It releases copper in the uterine cavity and stops implantation.
- The emergency IUD is the most effective method of emergency contraception – less than 1% of women who use the IUD get pregnant.
- It’s more effective than the emergency pill at preventing pregnancy after unprotected sex.
IUD can be used if:
- You have HIV
- You are breastfeeding
- Will not interfere with other medicines.
IUD cannot be used if:
- You have a problem with the cervix
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding.
- You have untreated sexually transmitted infections.
Side Effects of IUD
- Side effects of the IUD can be pain, infection
- Complications are rare, e.g. perforation through the uterus, or the IUD slips out of your womb.
Irrespective of which emergency contraceptive you use, you should see a gynecologist and discuss all the choices that are available for regular contraception and adopt a method that suits your needs.
Also Read: What are Emergency Contraception Methods?