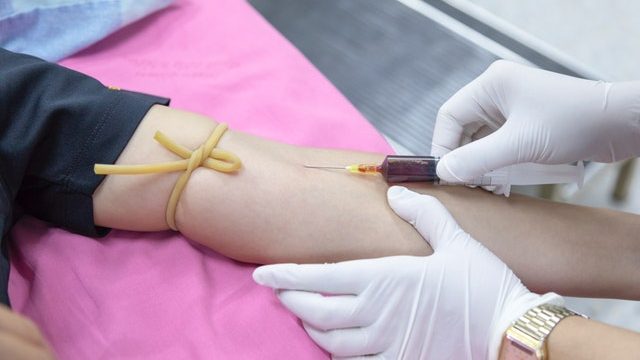
Rh Incompatibility in pregnancy is a concern to some women.
What is Rh factor?
The Rh factor is a protein that is inherited and that can be found on the surface of red blood cells.
Individuals who have the protein are known as Rh-Positive and those who do not have it are called Rh-Negative.
Every individual will inherit the Rh factor gene from the mother or the father.
In a case where the pregnant woman is Rh-negative and the father of the baby is Rh-positive, the baby has a 50 percent or more chance of having Rh-positive blood.
What is Rh Incompatibility and its impact on pregnancy?
Your pregnancy gets influenced by Rh Factor only in case the mother is Rh-negative, and the fetus is Rh-positive. In this case, Rh Incompatibility will develop.
- If the fetus is Rh-negative, then, in that case, there is no impact.
- When a woman who is Rh-negative is carrying an Rh-positive fetus, there is a possibility of the fetal blood getting into the maternal bloodstream.
Normally there is a barrier between maternal and fetal blood. The mixing commonly happens at the time of delivery and labor. It can happen under the following circumstances:
- During procedures such as amniocentesis
- Chorion villus sampling
- Fetal blood sampling
- Miscarriage
- Bleeding during pregnancy
- Induced abortion
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Trauma to the abdomen.
What are the risks of Rh Incompatibility?
When Rh-positive fetal blood enters the maternal bloodstream her body will recognize the Rh-positive cells as foreign antigens and will fight them by developing Rh antibodies. These antibodies can cross the placenta and destroy the fetal blood cells that are Rh-positive. This can lead to serious health problems such as:
- Anemia
- Jaundice in the newborn
- Generalized swelling
- Heart failure due to fluid retention and eventually even death in a fetus or newborn.
Second And Subsequent Pregnancies And Rh Incompatibility
The Rh incompatibility is more likely to manifest in second and subsequent pregnancies.
In the first pregnancy, the maternal blood meets fetal blood mainly at the time of labor and therefore does not have time to develop antibodies. However, the mother will develop antibodies very quickly in the next pregnancy when exposed to Rh-positive blood and then the fetus can get exposed to the antibodies for the full duration of the pregnancy. This can then lead to various complications.
How is Rh Incompatibility diagnosed?
Every pregnant woman undergoes a blood group check. If she is Rh positive, then no further testing is required.
If she is Rh-negative, then the blood group of the father of the baby is checked.
In case, he is also Rh-negative, then there is no possibility of incompatibility as the fetus cannot be Rh-positive.
If he is Rh-positive then there is a chance of Rh incompatibility. In this case, an antibody screening is done to assess if the mother has any antibodies to Rh-positive antigens.
In case antibodies are present, then further testing for levels is required and fetal monitoring is done to evaluate if the fetal cells are getting destroyed.
How can we prevent the risk in an Rh-negative blood group?
It is important to prevent the Rh-negative mother from developing antibodies to the Rh Antigen. Rh immunoglobulin injections can be given to the mother to stop her body from making antibodies. This injection is advocated in the following circumstances:
- Preventive At 28 weeks of pregnancy (as the blood group of the fetus is not known) within 72 hours after the birth of an Rh-positive baby (it is not required in case the baby is Rh-negative)
- After an ectopic pregnancy or a first trimester (threatened or inevitable or incomplete)
- Miscarriage
- Abortion after Invasive Procedures, such as amniocentesis, CVS, fetal blood sampling, or fetal surgery.
- Trauma to the abdomen during pregnancy
If the pregnant Rh-negative woman already has Rh antibodies, the injection will no longer help. Thus, a woman who has Rh-negative blood must be treated with Rh immune globulin:
- During and after each pregnancy
- After any other event that allows her blood to mix with Rh-positive blood.
What are the treatment options available to deal with Rh Incompatibility?
- This is required when the antibodies are crossing over to the fetus and damaging the red blood cells of the fetus.
- In case the fetus has anemia then early delivery may be required. In case anemia develops too early in pregnancy and delivery is not feasible then the fetus may require blood transfusion inside the uterus.
- After delivery, the baby may need blood transfusion until the baby can make its own cells and hemoglobin stabilize.
Always ensure that you are aware of your blood group especially in pregnancy.
In case you are Rh-negative then you should be aware of your partner’s blood group and take the necessary steps to prevent Rh incompatibility.
Take an appointment with Dr. Sangeeta Agrawal to be safe and healthy during your pregnancy.